CI/CD
Difference between CI and CD (and the other CD)
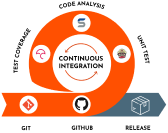
Continuous integration (CI) helps developers merge their code changes back to a shared branch, or “trunk,” more frequently—sometimes even daily. Once a developer's changes to an application are merged, those changes are validated by automatically building the application and running different levels of automated testing, typically unit and integration tests, to ensure the changes haven't broken the app.
This means testing everything from classes and functions to the different modules that comprise the entire app. If automated testing discovers a conflict between new and existing code, CI makes it easier to fix those bugs quickly and often.
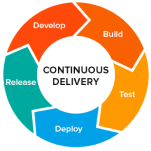
Following the automation of builds and unit and integration testing in CI, continuous delivery automates the release of that validated code to a repository. So, in order to have an effective continuous delivery process, it's important that CI is already built into your development pipeline. The goal of continuous delivery is to have a codebase that is always ready for deployment to a production environment.
In continuous delivery, every stage—from the merger of code changes to the delivery of production-ready builds—involves test automation and code release automation. At the end of that process, the operations team is able to deploy an app to production quickly and easily.
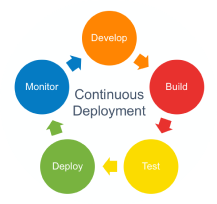
The final stage of a mature CI/CD pipeline is continuous deployment. As an extension of continuous delivery, which automates the release of a production-ready build to a code repository, continuous deployment automates releasing an app to production. Because there is no manual gate at the stage of the pipeline before production, continuous deployment relies heavily on well-designed test automation.
In practice, continuous deployment means that a developer's change to a cloud application could go live within minutes of writing it (assuming it passes automated testing). This makes it much easier to continuously receive and incorporate user feedback. Taken together, all of these connected CI/CD practices make deployment of an application less risky, whereby it's easier to release changes to apps in small pieces, rather than all at once. There's also a lot of upfront investment, though, since automated tests will need to be written to accommodate a variety of testing and release stages in the CI/CD pipeline.

Service discovery and load balancing
Continuous integration (CI) helps developers merge their code changes back to a shared branch, or “trunk,” more frequently—sometimes even daily. Once a developer's changes to an application are merged, those changes are validated by automatically building the application and running different levels of automated testing, typically unit and integration tests, to ensure the changes haven't broken the app.
This means testing everything from classes and functions to the different modules that comprise the entire app. If automated testing discovers a conflict between new and existing code, CI makes it easier to fix those bugs quickly and often.

Storage orchestration
Following the automation of builds and unit and integration testing in CI, continuous delivery automates the release of that validated code to a repository. So, in order to have an effective continuous delivery process, it's important that CI is already built into your development pipeline. The goal of continuous delivery is to have a codebase that is always ready for deployment to a production environment.
In continuous delivery, every stage—from the merger of code changes to the delivery of production-ready builds—involves test automation and code release automation. At the end of that process, the operations team is able to deploy an app to production quickly and easily.

Automated rollouts and rollbacks
The final stage of a mature CI/CD pipeline is continuous deployment. As an extension of continuous delivery, which automates the release of a production-ready build to a code repository, continuous deployment automates releasing an app to production. Because there is no manual gate at the stage of the pipeline before production, continuous deployment relies heavily on well-designed test automation.
In practice, continuous deployment means that a developer's change to a cloud application could go live within minutes of writing it (assuming it passes automated testing). This makes it much easier to continuously receive and incorporate user feedback. Taken together, all of these connected CI/CD practices make deployment of an application less risky, whereby it's easier to release changes to apps in small pieces, rather than all at once. There's also a lot of upfront investment, though, since automated tests will need to be written to accommodate a variety of testing and release stages in the CI/CD pipeline.

